What is JSON
JSON is a lightweight text-based open standard data-interchange format. It is human readable. JSON is derived from a subset of JavaScript programming language (Standard ECMA-262 3rd Edition—December 1999). It is entirely language independent and can be used with most of the modern programming languages.
JSON is often used to serialize and transfer data over a network connection, for example between the web server and a web application. In computer science, serialization is a process to transforming data structures and objects in a format suitable to be stored in a file or memory buffer or transmitted over a network connection. Later on, this data can be retrieved. Because of the very nature of the JSON, it is useful for storing or representing semi structured data
JSON is a standard and is specified on RFC4627 on IETF (International Engineering Task Force). The specification is made by Doglus Crockford on July 2006.
JSON files are saved with .json extension. Internet media type of JSON is "application/json".
What JSON looks like
We will now look how a typical JSON looks like. The following code snippet is a valid (you will see in a later chapter what is syntactically valid JSON) JSON representing information about a book.
Now we will discuss what are basic constructs of JSON.
Basic Constructs
- There four basic and built-in data types in JSON. They are strings, numbers, booleans (i.e true and false) and null. Besides, there are two data types which are structured - objects and arrays.
- Objects are wrapped within '{' and '}'. Arrays are enclosed by '[' and ']'. Objects are a list of label-value pairs. Arrays are list of values.
- Both objects and arrays can be nested.
- strings, numbers, booleans (i.e true and false) and null can be used as values.
The following image and then text following will be useful to get you started with how JSON data is constructed.
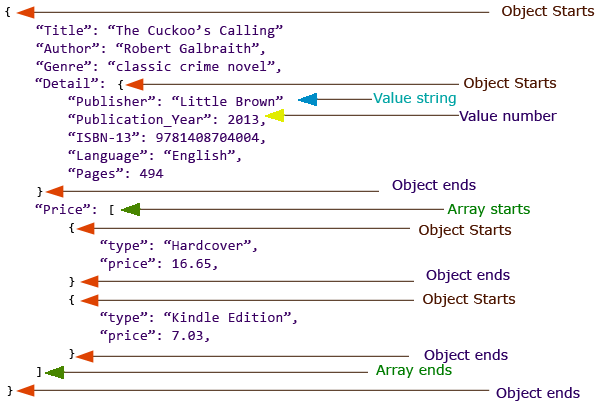
So the entire content of the JSON data shown above is enclosed within an object. "Title": "The Cuckoo's Calling", "Author": "Robert Galbraith", "Genre": "classic crime novel", these are label-value pairs separated by commas. Labels and their values are separated by a colon (:). Notice that both labels and values are enclosed by quotations, since they are strings.
Notice the '"Detail"' label then. It contains another object, which again contains several label-value pairs. This is an example of how nesting (object within object in this case) is done in JSON.
Then '"Price"' label contains an array, which is turn contains two separate objects. Another example of nesting.
Also, notice that numbers are not enclosed by quotations.
History of JSON
The name behind popularizing the JSON is Douglas Crockford. He used JSON is his company State Software around 2001.
In 2005, Yahoo started using JSON in it's web services.
In later 2006, Google started offering JSON in its Gdata web protocol.
Today, JSON is one of the most widely used data-interchange format in web, and supported by most of the Web APIs (like twitter api) to fetch public data and creating applications out of them.
Comparison with Relational Database
Since JSON is used to host/represent data, we will discuss how it is different from the traditional Relational Database model used in RDBMS systems like MySQL, SQL Server etc. This may be useful for you to choose JSON over RDBMS or RDBMS over JSON depending upon the type and structure of data you want to deal with. Let's start with a comparison against certain features:
- Structure : In the relational database, these are tables, which are responsible for storing data in form of rows and columns. JSON uses objects and arrays - objects are label-value pairs and arrays are the list of values. They can be nested recursively.
- Metadata : In a relational database, it is a schema, which is used for storing data about the structure and type of the data to be stored and schemas are predefined, i.e. they are created at the time of creation of database and tables before you can store data. JSON also may use schema, to have a definition of the structure and type of data to represented, but it is not predefined. Most of the time it is self-describing, even if it uses a schema, it comes with much more flexibility than a schema used in relational database. But it would be judgmental to say that it is an advantage of JSON over Relational Database. Having a pre-defined schema may have several benefits depending upon the data to be dealt with.
- Retrieving data : Relational databases use Structured Query Language, an expressive and very powerful language, based on relational algebra to fetch data from the database. JSON does not have any widely used or accepted language to query the data stored. JAQL and JSONiq are many of the query languages which mostly are work in progress to query data from JSON.
- Sorting : SQL does the job in case of Relational Database. In the case of JSON, since arrays often used, in programs, arrays can be sorted.
- Application : There are many open-source as well as commercial Relational Database systems are available - like MySQL, POstgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle, DB2 etc. JSON is mostly applied to programming languages. But, there is also NoSQL systems. NoSQL systems use JSON format to store data. Some of the NoSQL systems use JSON format are - MongoDB, CoucheDB etc.
- Learning curve: JSON is a clear winner here. Since the basic data types and structure used here are similar to those used in many programming languages, it is obvious that if you are coming from a programming background, you will pick things up in JSON pretty fast. RDBMS is a separate field of study on the other hand. But definitely, the time you invest in learning Relational database return you several opportunities and benefits
Now let's discuss a few use cases which will be useful.
Assume that you have to store information regarding students(name, id, class) and marks obtained by them in various subjects. Relational Database is suitable here than using JSON, since here we can have one table containing student detail and another table for marks obtained by them in various subjects.
Now assume that we have to represent information regarding students(name, id, class) and various projects they have completed in different subjects along with a brief description of the project. Assume that a student may complete any number of projects and any of number subjects they choose from. Notice that, in this case, you may have any uniformity of the data to be stored. So, in this case, JSON will be preferable than using Relational Database.
JSON vs XML
Since XML is also used as data interchange format widely, we will try to draw a comparison between them. The purpose of the comparison it's definitely not in the line of which is better, rather we will try to understand which one is suitable for storing specific kind of data.
- XML is more expressive than JSON. XML sometimes also suffers from using tags repeatedly, where as JSON is much more concise.
- XML is more complex than JSON.
- There are several specifications to define schema(metadata) for XML, for example DTD and XSD. JSON schema is there for doing the same for JSON, but it is not as widely used as XML schemas.
- XML can be used with most of the programming languages as JSON. But the point is, when you are working with XML, then you have you are actually trying match two systems those data structures are different. In the case of JSON though, since objects and arrays are basic data structures used, it is easy to work with them in programs.
- For selecting specific parts of an XML document, there is standard specification called XPath. This is widely used. In JSON, we have JSONPath to do the same, but not widely in use.
- XML has Xquery specification for querying XML data. JSON though have JAQL, JSONiq etc, but they are not in use widely.
- XML has XSLT specification which may be used to apply a style to an XML document. JSON does not have any such thing.
Typical uses of JSON
API : API is the most widely used area where JSON is used for data exchange. Specially, web applications those have a social face, it has become obvious now that they have an API, so that developers can consume the huge amount of data collected by the app and then can create derivative apps. Twitter, Facebook, Linkedin, Flicker, Dribble, you name it, all the well-known apps on the internet today has an API and uses JSON as their preferred format for serving data to the developers. Out of these APIs, some have support for both JSON and XML, but some support only JSON.
We will see a simple demonstration of rottentomatoes API to get a feel of how JSON is used in APIs. In this demo, we are querying the rottentomatoes.com for name and thumbnail poster of the movie containing the string "Life is beautiful" using JavaScript and Jquery. It returns the result in JSON format and then it is displayed on the browser. Following is a screenshot of it.
No comments:
Post a Comment